Despite a moderation in economic momentum, Cambodia’s growth prospects for 2025 and 2026 remain steady, supported by resilient performance across key sectors, according to the Ministry of Economy and Finance’s latest outlook.
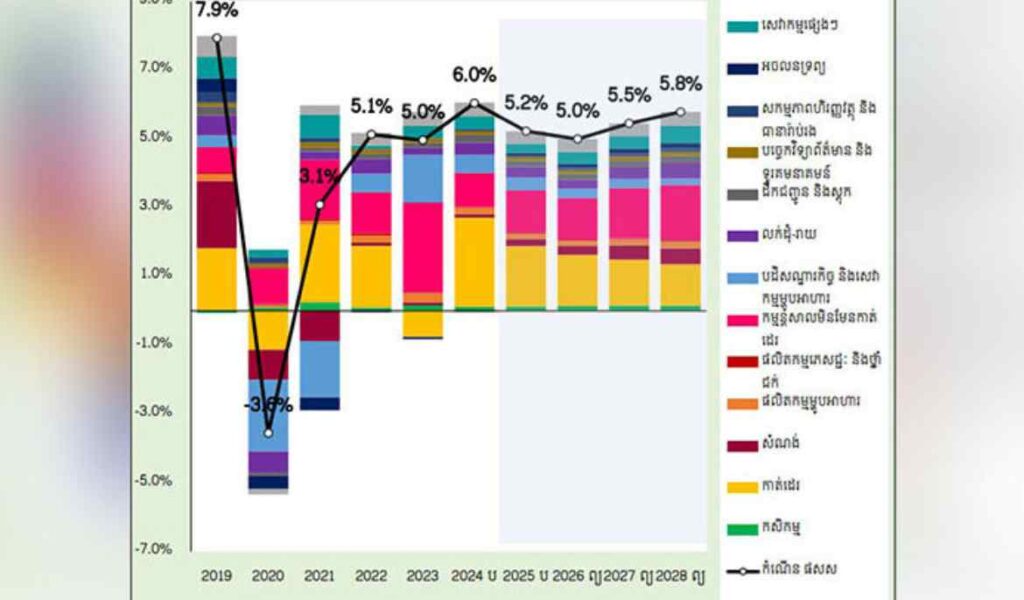
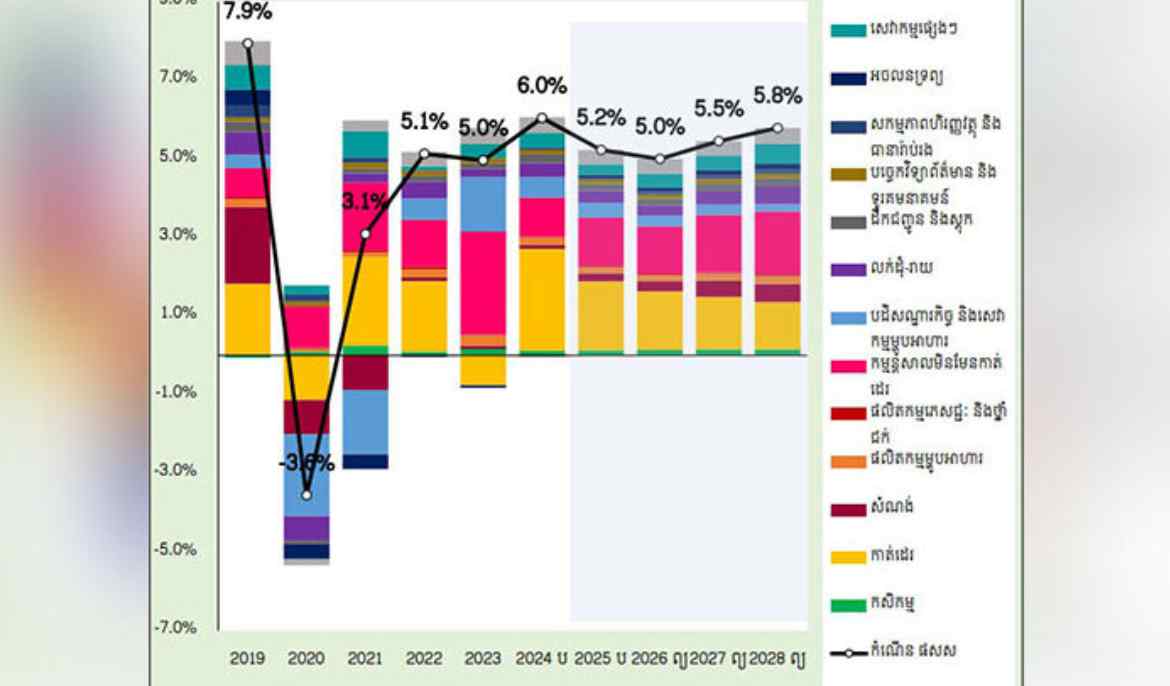
The Macroeconomic Situation and Outlook for 2025 and 2026 report, prepared by the Ministry’s General Department of Policy and released on Wednesday, projects GDP growth of 5.2 percent in 2025 and 5.0 percent in 2026. The projections are in line with the Medium-Term Fiscal Framework (2026-2028) published in May this year.
The assessment comes as the global economic outlook for the second half of 2025 improves slightly compared to earlier forecasts in April, driven by front-loaded exports ahead of tariff hikes and supportive policy measures in major economies such as China, South Korea, and Germany.
In Cambodia, growth will be anchored by agriculture, garment manufacturing, non-garment manufacturing, tourism and related services, wholesale and retail trade, and the construction and real estate sectors.
Agriculture is expected to record stable gains, buoyed by both crop production and the fishing industry. The garment sector will see strong growth in the first half of 2025 before easing in the latter half as US reciprocal tariffs take effect.
Non-garment manufacturing – particularly electronics, furniture, and tyre production – will maintain positive momentum, although industries catering to the domestic market may also face a slowdown in the second half due to countervailing duties.
Tourism and related services continue to expand, supported by a steady increase in both domestic and international arrivals. Wholesale and retail trade remain on an upward trajectory, though weaker purchasing power is beginning to weigh on sales volumes.
The construction and real estate sector is gradually recovering, with activity driven by high-end residential projects and industrial facilities. However, growth remains subdued compared to pre-pandemic peaks.
While challenges persist, the MEF report notes that Cambodia’s diversified growth drivers, coupled with prudent macroeconomic management, will help cushion the economy against external shocks.
However, Cambodia’s macroeconomic outlook for 2025 and 2026 remains clouded by heightened uncertainty, with trade disruptions, tariffs, and regional tensions emerging as key risks, according to MEF.
The report prepared by the MEF’s General Department of Policy warned that the situation has evolved more quickly than anticipated since the previous assessment in May.
One of the most pressing challenges is the 19 percent tariff rate impacting the private sector, particularly factories and enterprises. The report emphasises the need for urgent measures to help businesses diversify export markets beyond their heavy reliance on the United States, while simultaneously strengthening competitiveness and enhancing the industrial value chain.
h
Compounding the challenge is the continued closure of the Cambodia-Thailand land border, which has disrupted the flow of goods and production materials to industries dependent on the Thai market. The situation has also affected tourism flows—particularly Thai package tours—and triggered a sudden increase in returning migrant workers, adding pressure to the domestic labour market.
In response, the Royal Government is pursuing a dual strategy: addressing immediate and short-term disruptions while advancing medium- to long-term structural reforms.
Short-term priorities include targeted interventions to ease production chain bottlenecks, support returning workers and border communities, and redirect agricultural exports to alternative markets.
Medium- and long-term measures will focus on diversifying export markets, boosting industrial value chains, and promoting the growth of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups. Public financial policy will remain prudent yet flexible, with an emphasis on cost efficiency and sustainability. Monetary policy will aim to safeguard financial stability, encourage credit growth in productive sectors, and carefully manage price and exchange rate conditions.